Until now, AI services based on large language models (LLMs) have mostly relied on expensive data center GPUs. This has resulted in high operational costs and created a significant barrier to entry for utilizing AI technology. A research team at KAIST has developed a technology that reduces reliance on expensive data center GPUs by utilizing affordable, everyday GPUs to provide AI services at a much lower cost.
The research team led by Professor Dongsu Han from the School of Electrical Engineering developed "SpecEdge," a new technology that significantly lowers LLM infrastructure costs by utilizing affordable, consumer-grade GPUs widely available outside of data centers.
How SpecEdge technology works
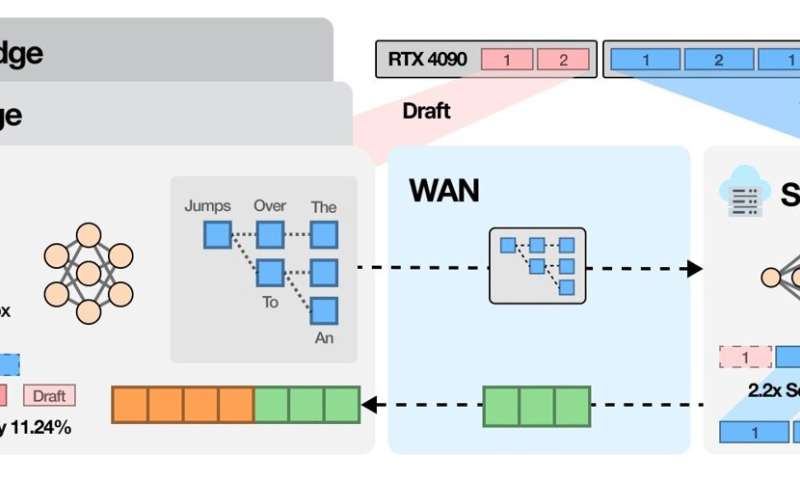
SpecEdge is a system where data center GPUs and "edge GPUs"—found in personal PCs or small servers—collaborate to form an LLM inference infrastructure. By applying this technology, the team successfully reduced the cost per token (the smallest unit of text generated by AI) by approximately 67.6% compared to methods using only data center GPUs.
To achieve this, the research team utilized a method called "Speculative Decoding." In this process, a small language model placed on the edge GPU quickly generates a high-probability token sequence (a series of words or word fragments). Then, the large-scale language model in the data center verifies this sequence in batches. During this process, the edge GPU continues to generate words without waiting for the server's response, simultaneously increasing LLM inference speed and infrastructure efficiency.

Compared to performing speculative decoding solely on data center GPUs, SpecEdge improved cost efficiency by 1.91 times and server throughput by 2.22 times. Notably, the technology was confirmed to work seamlessly even under standard internet speeds, meaning it can be immediately applied to real-world services without requiring a specialized network environment.
Furthermore, the server is designed to efficiently process verification requests from multiple edge GPUs, allowing it to handle more simultaneous requests without GPU idle time. This has realized an LLM serving infrastructure structure that utilizes data center resources more effectively.
Research recognition and future impact
Dr. Jinwoo Park and M.S candidate Seunggeun Cho from KAIST participated in this study. The research results were presented as a "Spotlight" (top 3.2% of papers, with a 24.52% acceptance rate) at the NeurIPS 2025 conference, held in San Diego from December 2–7. The paper, titled "SpecEdge: Scalable Edge-Assisted Serving Framework for Interactive LLMs," is available on the arXiv preprint server.
This research presents a new possibility for distributing LLM computations—which were previously concentrated in data centers—to the edge, thereby reducing infrastructure costs and increasing accessibility. In the future, as this expands to various edge devices such as smartphones, personal computers, and Neural Processing Units (NPUs), high-quality AI services are expected to become available to a broader range of users.

Professor Dongsu Han, who led the research, stated, "Our goal is to utilize edge resources around the user, beyond the data center, as part of the LLM infrastructure. Through this, we aim to lower AI service costs and create an environment where anyone can utilize high-quality AI."
More information: Jinwoo Park et al, SpecEdge: Scalable Edge-Assisted Serving Framework for Interactive LLMs, arXiv (2025). DOI: 10.48550/arxiv.2505.17052
Citation: Turning PCs and mobile devices into AI infrastructure can slash operational costs (2026, January 2) retrieved 3 January 2026 from https://techxplore.com/news/2026-01-pcs-mobile-devices-ai-infrastructure.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.